Class D Power Amplifiers honeywellvoicealarm.com 1.5.3 Class D 9 1.5.4 Class E IO 1.5.5 Class F 10 1.5.6 Opriniuni Clmice for a Pawer Amplifier Arcftirecture 12 1.6 Previous Work 12 i $7 Objectives and Ourline of the Thesis 13 1.8 Re ferences 15 CHAPTER 3 Class-E Power Amplifier Design 16 2.1 Introduction 16 2.2 Class E Theory of Operation 18 7.3 Class-E Amplifier Design 23
Power Amplifiers Tutorialspoint
Designing Practical High Performance Class D Audio Amplifier. An amplifier is an electronic device used to increase the magnitude of voltage/current/power of an input signal. It takes in a weak electrical signal/waveform and reproduces a similar stronger waveform at the output by using an external power source. Depending on the changes it makes to the input signal, amplifiers are broadly classified into Current, …, TPA3113D2 6-W Filter-Free Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier With SpeakerGuard™ 1 1 Features 1• 6-W/ch into an 8-ΩLoads at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 12-W into a 4-ΩMono Load at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 87% Efficient Class-D Operation Eliminates Need for Heat Sinks • Wide Supply Voltage Range Allows Operation from 8 V to.
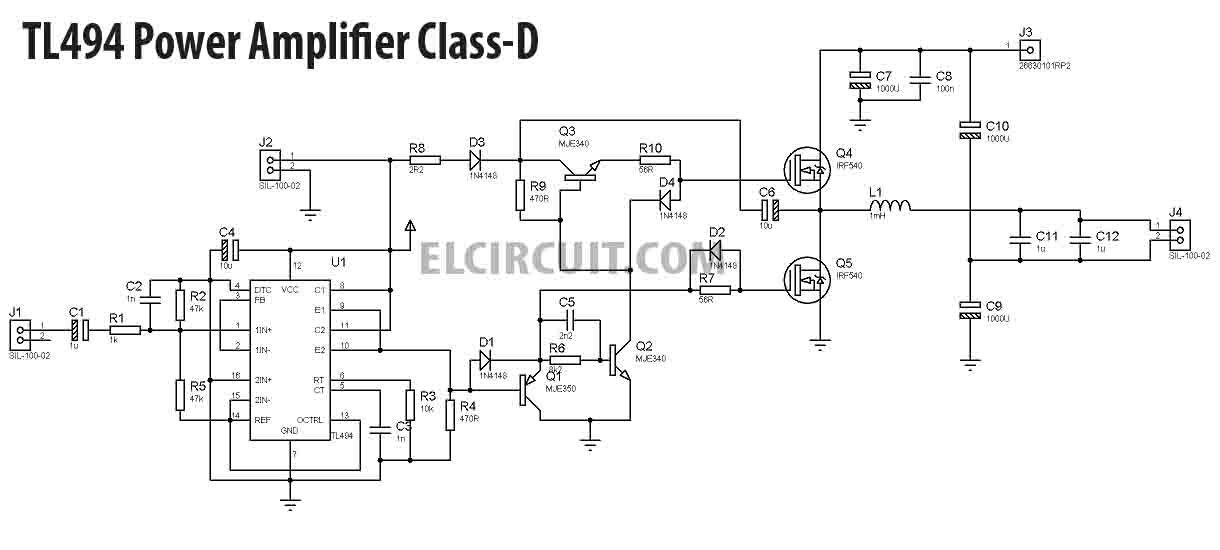
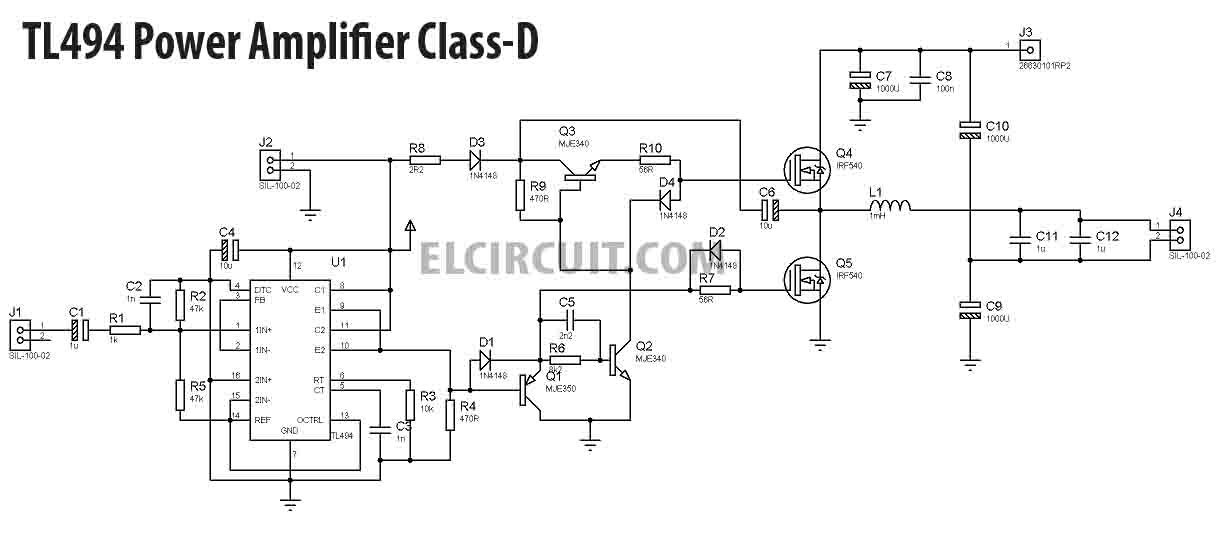
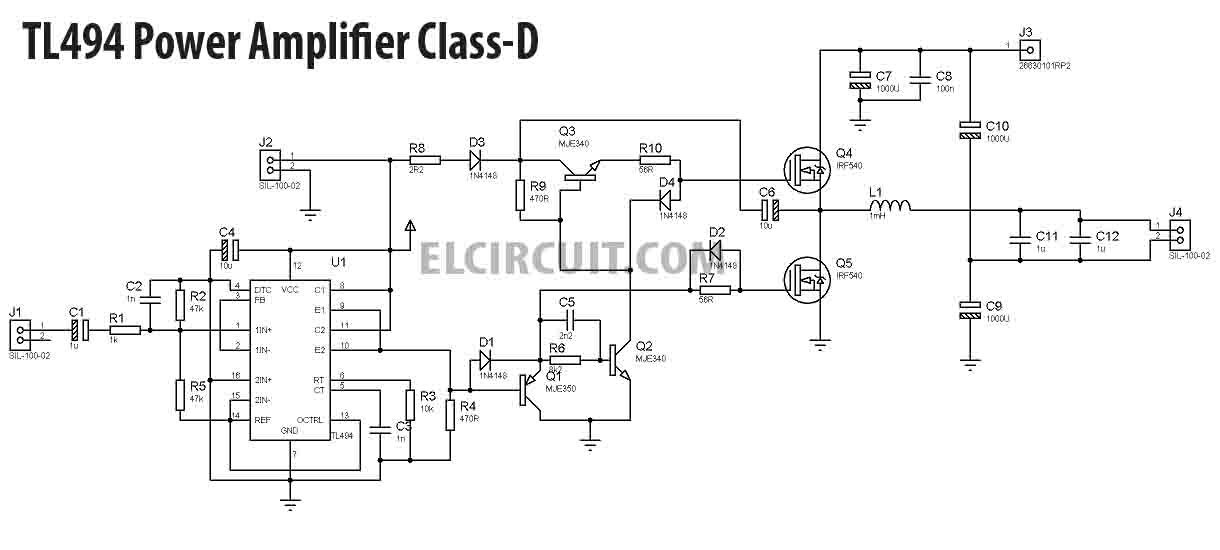
25/03/2018В В· In this project, I will share about class-d power amplifier using TL494 IC for PWM, and use N-Channel MOSFET transistor as the final amplifier. This circuit is not so complicated and cheap to make practice making power amplifier class-d. This power amplifier circuit can be supplied with 30V to 100V DC asymmetric power supply using 8VDC bias The two-channel Class D audio amplifier currently holds the largest market share and is expected to grow at the highest rate during the forecast period, as it is commonly used in in-car audio and
Power Amplifier. The function of a power amplifier is to raise the power level of input signal. It is required to deliver a large amount of power and has to handle large current. The characteristics of a power amplifier are as follows в€’ The base of transistor is made thicken to handle large currents. The value of ОІ being (ОІ > 100) high. 11/12/2018В В· Class D amplifier is the highest power efficient amplifier class in the A, B, AB, and C and D segment. It has smaller heat dissipation, so small heatsink is needed. The circuit requires various switching components like MOSFETs which has low on resistance.
A Brief History of Power Amplifiers Power amplifier architectures The three-stage structure The two-stage amplifier structure Power amplification classes Class-A Class-AB Class-B Class-C Class-D Class-E Class-F Class-G Class-H Class-S Variations on Class-B AC and DC coupled amplifiers The advantages of AC-coupling The advantages of DC-coupling A Brief History of Power Amplifiers Power amplifier architectures The three-stage structure The two-stage amplifier structure Power amplification classes Class-A Class-AB Class-B Class-C Class-D Class-E Class-F Class-G Class-H Class-S Variations on Class-B AC and DC coupled amplifiers The advantages of AC-coupling The advantages of DC-coupling
Amplifier Efficiency The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. In general terms, we see that a class A amplifier, with dc bias at one-half the supply voltage level, uses a good amount of power to maintain bias, even with no input signal Class D Amplifier. Linear Mode Power Amplifiers – Class A, B, AB and class C are all linear mode amplifiers that have an output that is proportional to their input. Linear mode amplifiers do not saturate, fully turn-on or fully turn-off. Since the transistors are always conducting, heat is generated and continuously consuming power.
1.5.3 Class D 9 1.5.4 Class E IO 1.5.5 Class F 10 1.5.6 Opriniuni Clmice for a Pawer Amplifier Arcftirecture 12 1.6 Previous Work 12 i $7 Objectives and Ourline of the Thesis 13 1.8 Re ferences 15 CHAPTER 3 Class-E Power Amplifier Design 16 2.1 Introduction 16 2.2 Class E Theory of Operation 18 7.3 Class-E Amplifier Design 23 The most commonly used type of power amplifier configuration is the Class A Amplifier. The Class A amplifier is the simplest form of power amplifier that uses a single switching transistor in the standard common emitter circuit configuration as seen previously to produce an inverted output. The transistor is always biased “ON” so that it
• Class D Power Amplifier operation. • Class E & F Power Amplifiers. • Class G & H Power Amplifiers. 5.7 Power Amplifiers Quiz. • Test your knowledge and understanding of Power Amplifiers. www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Amplifiers AMPLIFIERS MODULE 05.PDF 2 E. COATES 2007 - 2017 The voltage amplifiers described in Amplifiers Modules 1 to 4 can increase the amplitude of a signal So there is a high probability that your garage door remote control is equipped with a Class-C RF amplifier. CLASS D Class D is currently the best solution for any low-cost, high-power, low-frequency amplifier—particularly for audio applications. Figure 5 shows its simple concept.
So there is a high probability that your garage door remote control is equipped with a Class-C RF amplifier. CLASS D Class D is currently the best solution for any low-cost, high-power, low-frequency amplifier—particularly for audio applications. Figure 5 shows its simple concept. Class D: This operating class is a form of amplifier operation using pulse (digital) signals, which are on for a short interval and off for a longer interval. Power Amplifier Classes … • The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D.
Download Carvin power amplifier schematics here. 1.5.3 Class D 9 1.5.4 Class E IO 1.5.5 Class F 10 1.5.6 Opriniuni Clmice for a Pawer Amplifier Arcftirecture 12 1.6 Previous Work 12 i $7 Objectives and Ourline of the Thesis 13 1.8 Re ferences 15 CHAPTER 3 Class-E Power Amplifier Design 16 2.1 Introduction 16 2.2 Class E Theory of Operation 18 7.3 Class-E Amplifier Design 23
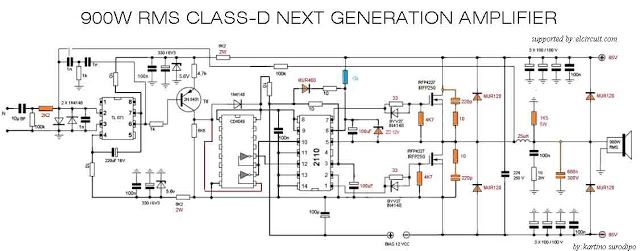
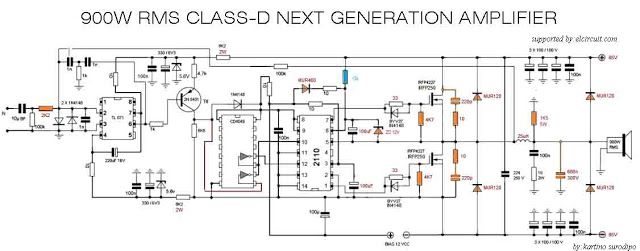
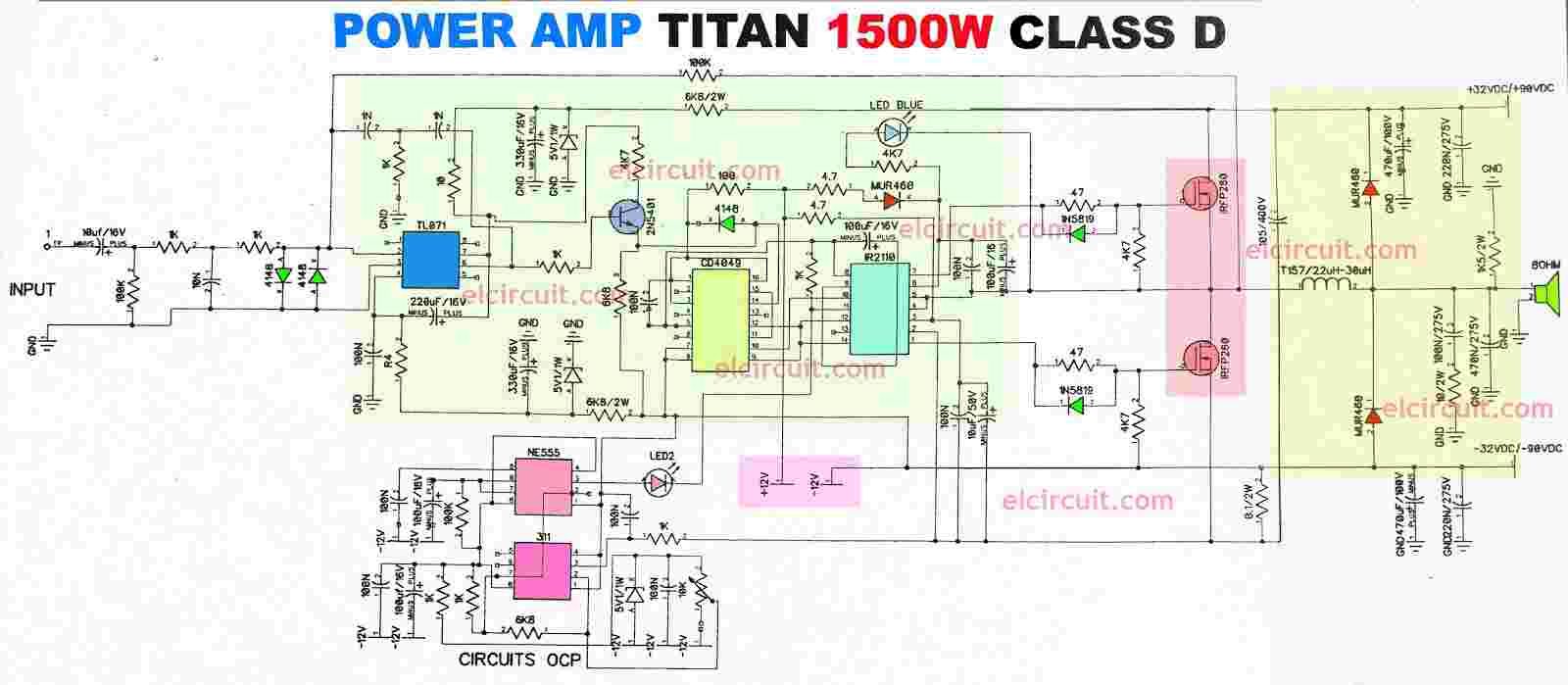
Power Amplifiers • Purpose of a power amplifier –Generate high output power –Efficient conversion of DC power to RF power –Linear amplification • Generally PAs will be –Common source –Cascode • Inductor is a “choke” to provide D • apacitor is a “ac coupling” path to output ©James Buckwalter 2 05/12/2018 · This High Power Amplifier circuit is a class D power amplifier, which has a high enough power to generate 3000W of power at 4 Ohm impedance - and also more power up to 4500W at 2 Ohm impedance. See schematic and PCB Layout here.
Power amplifier classes. Power amplifier circuits (output stages) are classified as A, B, AB and C for analog designs—and class D and E for switching designs. The classes are based on the proportion of each input cycle (conduction angle) during which an amplifying device passes current. The image of the conduction angle derives from amplifying a sinusoidal signal. 05/12/2018 · This High Power Amplifier circuit is a class D power amplifier, which has a high enough power to generate 3000W of power at 4 Ohm impedance - and also more power up to 4500W at 2 Ohm impedance. See schematic and PCB Layout here.
Power Amplifier Schematics Carvin Amps and Audio

MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier. The most commonly used type of power amplifier configuration is the Class A Amplifier. The Class A amplifier is the simplest form of power amplifier that uses a single switching transistor in the standard common emitter circuit configuration as seen previously to produce an inverted output. The transistor is always biased “ON” so that it, Any power losses associated with a Class D amplifier are primarily attributed to output transistor on-resistances, switching losses, and quiescent current overhead. Most power lost in an amplifier is dissipated as heat. Because heatsink requirements can be greatly reduced or eliminated in Class D amplifiers, they are ideal for compact high-power.
Class D Audio. Power amplifier classes. Power amplifier circuits (output stages) are classified as A, B, AB and C for analog designs—and class D and E for switching designs. The classes are based on the proportion of each input cycle (conduction angle) during which an amplifying device passes current. The image of the conduction angle derives from amplifying a sinusoidal signal., well-designed low-to-moderate-power Class AB amplifiers can make them competitive with Class D amplifiers. Class D power dissipation is unquestionably superior for the higher output power ranges, though. Class D Amplifier Terminology, and Differential vs. Single-Ended Versions Figure 3 shows a differential implementation of the output.
MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier
Amplifier Classes from A to H Circuit Cellar. Download Carvin power amplifier schematics here. Class D Power Amplifiers The D400 and D250 voice alarm power amplifiers comprise of two independent amplifier channels with 100 V output compatible with the Honeywell Voice Alarm System. The power amplifiers are controlled and monitored by the DOM4-8 (Digital Output Module) and DOM4-24 modules. Voice Alarm Key Features: l Power amplifier, 2.
1.5.3 Class D 9 1.5.4 Class E IO 1.5.5 Class F 10 1.5.6 Opriniuni Clmice for a Pawer Amplifier Arcftirecture 12 1.6 Previous Work 12 i $7 Objectives and Ourline of the Thesis 13 1.8 Re ferences 15 CHAPTER 3 Class-E Power Amplifier Design 16 2.1 Introduction 16 2.2 Class E Theory of Operation 18 7.3 Class-E Amplifier Design 23 Comparison chart for Class ab Amplifier vs Class d Here, I am going to present a comparison chart between these two amplifiers, Class AB and class D. So, in case of any kind of guidance related to these amplifiers you can check out this chart and if you do not know about these amplifiers and are confused between the selections, then this chart will help you anyway.
Class D Audio Amplifier Design • Class D Amplifier Introduction • Gate Driver • MOSFET • Package • Design Example Theory of Class D operation, topology comparison How to drive the gate, key parameters in gate drive stage How to choose, tradeoff relationships, loss calculation Importance of layout and package, new packaging technology History. The first Class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. However, it had an output power of only 2.5 watts.The Sinclair X-20 in 1966 produced 20 watts, but suffered from the inconsistencies and limitations of the
25/03/2018 · In this project, I will share about class-d power amplifier using TL494 IC for PWM, and use N-Channel MOSFET transistor as the final amplifier. This circuit is not so complicated and cheap to make practice making power amplifier class-d. This power amplifier circuit can be supplied with 30V to 100V DC asymmetric power supply using 8VDC bias Class D Audio Amplifier Design • Class D Amplifier Introduction • Gate Driver • MOSFET • Package • Design Example Theory of Class D operation, topology comparison How to drive the gate, key parameters in gate drive stage How to choose, tradeoff relationships, loss calculation Importance of layout and package, new packaging technology
Class A power amplifier is the simplest of all power amplifier configurations. They have high fidelity and are totally immune to crossover distortion. Even though the class A power amplifier have a handful of good feature, they are not the prime choice because of their poor efficiency. Since the active elements (transistors) are forward biased [PDF](en) Nathan O. Sokal, Class-E RF Power Amplifiers, QEX, janvier/février 2001 [PDF](en) RF Power Amplifiers Cours d'Alan Poon et Alan Siu Kei pour l'université de Toronto (en) Rane audio’s guide to amplifier classes [PDF](en) Power amplifiers sur le site de Silesian University of Technology
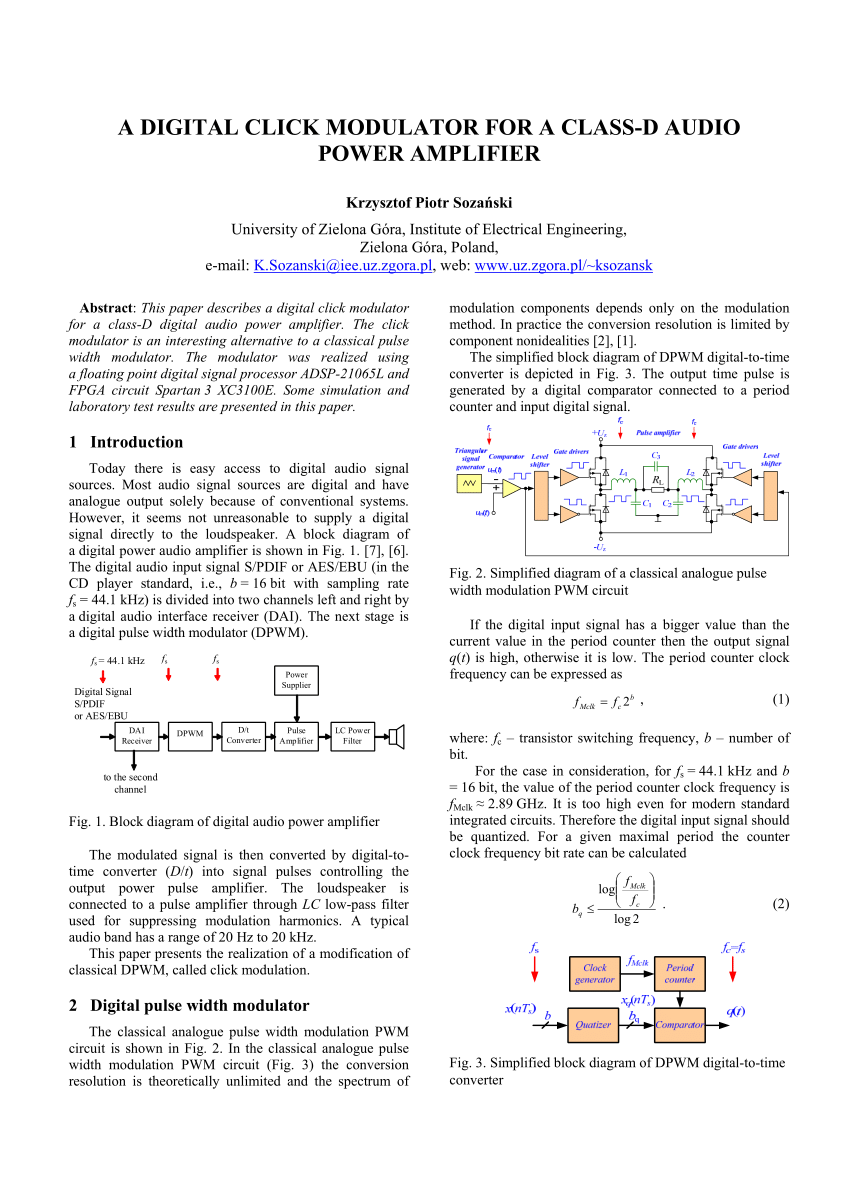
The class-D amplifier or inverter is composed of power MOSFETs, type IRFP460, in a full bridge configuration driven by IR2110 circuits in bootstrap mode. The specific nature of the problem comes power consumption are important for portability and battery use. This report discusses the design of a Class D audio amplifier that, at 80 Watts, is powerful enough to facilitate a small concert while maintaining 90% efficiency for lower energy usage and costs. With the growing
Class-D and Class-AB speaker amplifiers, with analog and digital inputs, scalable output power and ranging supply voltages for your next audio design. 25/03/2018В В· In this project, I will share about class-d power amplifier using TL494 IC for PWM, and use N-Channel MOSFET transistor as the final amplifier. This circuit is not so complicated and cheap to make practice making power amplifier class-d. This power amplifier circuit can be supplied with 30V to 100V DC asymmetric power supply using 8VDC bias
TPA3113D2 6-W Filter-Free Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier With SpeakerGuard™ 1 1 Features 1• 6-W/ch into an 8-ΩLoads at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 12-W into a 4-ΩMono Load at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 87% Efficient Class-D Operation Eliminates Need for Heat Sinks • Wide Supply Voltage Range Allows Operation from 8 V to The class-D amplifier or inverter is composed of power MOSFETs, type IRFP460, in a full bridge configuration driven by IR2110 circuits in bootstrap mode. The specific nature of the problem comes
Class D Audio Amplifier Design • Class D Amplifier Introduction • Gate Driver • MOSFET • Package • Design Example Theory of Class D operation, topology comparison How to drive the gate, key parameters in gate drive stage How to choose, tradeoff relationships, loss calculation Importance of layout and package, new packaging technology Amplifier Efficiency The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. In general terms, we see that a class A amplifier, with dc bias at one-half the supply voltage level, uses a good amount of power to maintain bias, even with no input signal
A Brief History of Power Amplifiers Power amplifier architectures The three-stage structure The two-stage amplifier structure Power amplification classes Class-A Class-AB Class-B Class-C Class-D Class-E Class-F Class-G Class-H Class-S Variations on Class-B AC and DC coupled amplifiers The advantages of AC-coupling The advantages of DC-coupling DIY 500w Class D amplifier circuit using TL494 ic. it is a class-d tl494 switching amplifier with high efficiency. You can use it as a car sub amp.
Power Amplifiers . Amplifier circuits form the basis of most electronic systems, many of which need to produce high power to drive some output device. Audio amplifier output power may be anything from less than 1 Watt to several hundred Watts. Radio frequency amplifiers used in transmitters can be required to produce thousands of kilowatts of Class-D PAs use two or more transistors as switches to generate a square drain-voltage waveform. A series-tuned output filter passes only the fundamental-frequency component to the load, Class-D amplifier Class-D Voltage and Current waveforms Class-D amplifiers suffer from a number of problems that make them difficult to realize,
The Class-D Ampli fier (From the book Introduction to Electroacoustics and Audio Ampli fier Design, Second Edition - Revised Printing, by W. Marshall Leach, Jr., published by Kendall/Hunt, °c 2001.) A class-D amplifier is one in which the output transistors are operated as switches. When a transistor is off, the current through it is zero The most commonly used type of power amplifier configuration is the Class A Amplifier. The Class A amplifier is the simplest form of power amplifier that uses a single switching transistor in the standard common emitter circuit configuration as seen previously to produce an inverted output. The transistor is always biased “ON” so that it
MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier
Speaker Amplifiers Class-D Overview Audio TI.com. Comparison chart for Class ab Amplifier vs Class d Here, I am going to present a comparison chart between these two amplifiers, Class AB and class D. So, in case of any kind of guidance related to these amplifiers you can check out this chart and if you do not know about these amplifiers and are confused between the selections, then this chart will help you anyway., MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier ˜˜ 19-6311; Rev 1; 7/13 General Description. The MAX98356 is a digital pulse-density modulated (PDM) input Class D power amplifier that provides Class . AB audio performance with Class D efficiency. This IC ….
TL494 Class D Amplifier Circuit 500w Amplifier
Classes de fonctionnement d'un amplificateur. Power Amplifier. The function of a power amplifier is to raise the power level of input signal. It is required to deliver a large amount of power and has to handle large current. The characteristics of a power amplifier are as follows в€’ The base of transistor is made thicken to handle large currents. The value of ОІ being (ОІ > 100) high., Comparison chart for Class ab Amplifier vs Class d Here, I am going to present a comparison chart between these two amplifiers, Class AB and class D. So, in case of any kind of guidance related to these amplifiers you can check out this chart and if you do not know about these amplifiers and are confused between the selections, then this chart will help you anyway..
power consumption are important for portability and battery use. This report discusses the design of a Class D audio amplifier that, at 80 Watts, is powerful enough to facilitate a small concert while maintaining 90% efficiency for lower energy usage and costs. With the growing History. The first Class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. However, it had an output power of only 2.5 watts.The Sinclair X-20 in 1966 produced 20 watts, but suffered from the inconsistencies and limitations of the
11/12/2018В В· Class D amplifier is the highest power efficient amplifier class in the A, B, AB, and C and D segment. It has smaller heat dissipation, so small heatsink is needed. The circuit requires various switching components like MOSFETs which has low on resistance. History. The first Class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. However, it had an output power of only 2.5 watts.The Sinclair X-20 in 1966 produced 20 watts, but suffered from the inconsistencies and limitations of the
Class-D PAs use two or more transistors as switches to generate a square drain-voltage waveform. A series-tuned output filter passes only the fundamental-frequency component to the load, Class-D amplifier Class-D Voltage and Current waveforms Class-D amplifiers suffer from a number of problems that make them difficult to realize, A Brief History of Power Amplifiers Power amplifier architectures The three-stage structure The two-stage amplifier structure Power amplification classes Class-A Class-AB Class-B Class-C Class-D Class-E Class-F Class-G Class-H Class-S Variations on Class-B AC and DC coupled amplifiers The advantages of AC-coupling The advantages of DC-coupling
With a class-D amplifier we seek to make at least one of these parameters zero at any given time, therefore making the power dissipated by the amplifier zero. The theoretical efficiency of a “perfect” linear amplifier is 78.5%. Now compare this to the theoretical efficiency of a “perfect” class-D amplifier which is 100%! You can never Class A Power Amplifiers - We have already come across the details of transistor biasing, which is very important for the operation of a transistor as an amplifier. Hence to achieve faith
Power amplifier classes. Power amplifier circuits (output stages) are classified as A, B, AB and C for analog designs—and class D and E for switching designs. The classes are based on the proportion of each input cycle (conduction angle) during which an amplifying device passes current. The image of the conduction angle derives from amplifying a sinusoidal signal. Class D Amplifier Fig 3 Linear and Class D Amplifier Efficiencies Gain – With Linear amplifiers the gain is con-stant irrespective of bus voltage variations, how-ever with Class D amplifiers the gain is propor-tional to the bus voltage. This means that the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) of a Class D amplifier is 0dB, whereas the PSRR of
The two-channel Class D audio amplifier currently holds the largest market share and is expected to grow at the highest rate during the forecast period, as it is commonly used in in-car audio and New Audio Power Amplifier (150115, PCB 150115-1 v2.1) It’s been three years since we presented our Q-Watt amplifier (110656). It’s a standard Class AB amplifier with a lot of power and low distortion.. Here we present a fairly simple Class D amplifier, although at first glance the schematic may make one think otherwise. A large part of the
The Class-D Ampli fier (From the book Introduction to Electroacoustics and Audio Ampli fier Design, Second Edition - Revised Printing, by W. Marshall Leach, Jr., published by Kendall/Hunt, °c 2001.) A class-D amplifier is one in which the output transistors are operated as switches. When a transistor is off, the current through it is zero [PDF](en) Nathan O. Sokal, Class-E RF Power Amplifiers, QEX, janvier/février 2001 [PDF](en) RF Power Amplifiers Cours d'Alan Poon et Alan Siu Kei pour l'université de Toronto (en) Rane audio’s guide to amplifier classes [PDF](en) Power amplifiers sur le site de Silesian University of Technology
An amplifier is an electronic device used to increase the magnitude of voltage/current/power of an input signal. It takes in a weak electrical signal/waveform and reproduces a similar stronger waveform at the output by using an external power source. Depending on the changes it makes to the input signal, amplifiers are broadly classified into Current, … Power amplifier classes. Power amplifier circuits (output stages) are classified as A, B, AB and C for analog designs—and class D and E for switching designs. The classes are based on the proportion of each input cycle (conduction angle) during which an amplifying device passes current. The image of the conduction angle derives from amplifying a sinusoidal signal.
The Class-D Ampli fier (From the book Introduction to Electroacoustics and Audio Ampli fier Design, Second Edition - Revised Printing, by W. Marshall Leach, Jr., published by Kendall/Hunt, °c 2001.) A class-D amplifier is one in which the output transistors are operated as switches. When a transistor is off, the current through it is zero Class D: This operating class is a form of amplifier operation using pulse (digital) signals, which are on for a short interval and off for a longer interval. Power Amplifier Classes … • The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D.
Class D power amplifier. Class D power amplifier is a type of audio amplifier were the power handling devices are operated as binary switches. Since the power handling devices (MOSFETS) works as perfect binary switches, no time is wasted in between the transition of stages and no power … • Class D Power Amplifier operation. • Class E & F Power Amplifiers. • Class G & H Power Amplifiers. 5.7 Power Amplifiers Quiz. • Test your knowledge and understanding of Power Amplifiers. www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Amplifiers AMPLIFIERS MODULE 05.PDF 2 E. COATES 2007 - 2017 The voltage amplifiers described in Amplifiers Modules 1 to 4 can increase the amplitude of a signal
How to Design a Class-D Amplifier Hephaestus Audio
Class A Power Amplifier Circuit Theory Design. Class A power amplifier is the simplest of all power amplifier configurations. They have high fidelity and are totally immune to crossover distortion. Even though the class A power amplifier have a handful of good feature, they are not the prime choice because of their poor efficiency. Since the active elements (transistors) are forward biased, So there is a high probability that your garage door remote control is equipped with a Class-C RF amplifier. CLASS D Class D is currently the best solution for any low-cost, high-power, low-frequency amplifier—particularly for audio applications. Figure 5 shows its simple concept..
The Class-D Ampli Georgia Institute of Technology

Class A Amplifier is a Class-A Transistor Amplifier. MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier ˜˜ 19-6311; Rev 1; 7/13 General Description. The MAX98356 is a digital pulse-density modulated (PDM) input Class D power amplifier that provides Class . AB audio performance with Class D efficiency. This IC … The Class-D Ampli fier (From the book Introduction to Electroacoustics and Audio Ampli fier Design, Second Edition - Revised Printing, by W. Marshall Leach, Jr., published by Kendall/Hunt, °c 2001.) A class-D amplifier is one in which the output transistors are operated as switches. When a transistor is off, the current through it is zero.

Class-D and Class-AB speaker amplifiers, with analog and digital inputs, scalable output power and ranging supply voltages for your next audio design. The two-channel Class D audio amplifier currently holds the largest market share and is expected to grow at the highest rate during the forecast period, as it is commonly used in in-car audio and
TPA3113D2 6-W Filter-Free Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier With SpeakerGuard™ 1 1 Features 1• 6-W/ch into an 8-ΩLoads at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 12-W into a 4-ΩMono Load at 10% THD+N From a 10-V Supply • 87% Efficient Class-D Operation Eliminates Need for Heat Sinks • Wide Supply Voltage Range Allows Operation from 8 V to Any power losses associated with a Class D amplifier are primarily attributed to output transistor on-resistances, switching losses, and quiescent current overhead. Most power lost in an amplifier is dissipated as heat. Because heatsink requirements can be greatly reduced or eliminated in Class D amplifiers, they are ideal for compact high-power
Amplifier Efficiency The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. In general terms, we see that a class A amplifier, with dc bias at one-half the supply voltage level, uses a good amount of power to maintain bias, even with no input signal MAX98356 PDM Input Class D Audio Power Amplifier ˜˜ 19-6311; Rev 1; 7/13 General Description. The MAX98356 is a digital pulse-density modulated (PDM) input Class D power amplifier that provides Class . AB audio performance with Class D efficiency. This IC …
Any power losses associated with a Class D amplifier are primarily attributed to output transistor on-resistances, switching losses, and quiescent current overhead. Most power lost in an amplifier is dissipated as heat. Because heatsink requirements can be greatly reduced or eliminated in Class D amplifiers, they are ideal for compact high-power Power Amplifiers • Purpose of a power amplifier –Generate high output power –Efficient conversion of DC power to RF power –Linear amplification • Generally PAs will be –Common source –Cascode • Inductor is a “choke” to provide D • apacitor is a “ac coupling” path to output ©James Buckwalter 2
The most commonly used type of power amplifier configuration is the Class A Amplifier. The Class A amplifier is the simplest form of power amplifier that uses a single switching transistor in the standard common emitter circuit configuration as seen previously to produce an inverted output. The transistor is always biased “ON” so that it Class D power amplifier. Class D power amplifier is a type of audio amplifier were the power handling devices are operated as binary switches. Since the power handling devices (MOSFETS) works as perfect binary switches, no time is wasted in between the transition of stages and no power …
25/03/2018В В· In this project, I will share about class-d power amplifier using TL494 IC for PWM, and use N-Channel MOSFET transistor as the final amplifier. This circuit is not so complicated and cheap to make practice making power amplifier class-d. This power amplifier circuit can be supplied with 30V to 100V DC asymmetric power supply using 8VDC bias 2 Г— 210 W class-D power amplifier The TDA8953 single-chip Class D amplifier contains high-power switches, drivers, timing and handshaking between the power switches, along with some control logic. To ensure maximum system robustness, an advanced protection strategy has been implemented to
[PDF](en) Nathan O. Sokal, Class-E RF Power Amplifiers, QEX, janvier/février 2001 [PDF](en) RF Power Amplifiers Cours d'Alan Poon et Alan Siu Kei pour l'université de Toronto (en) Rane audio’s guide to amplifier classes [PDF](en) Power amplifiers sur le site de Silesian University of Technology The two-channel Class D audio amplifier currently holds the largest market share and is expected to grow at the highest rate during the forecast period, as it is commonly used in in-car audio and
04/06/2017 · In this project I will show you why a class AB amplifier is pretty inefficient and how a class D amplifier on the other hand improves this efficiency. At the end I will show you how we can apply • Class D Power Amplifier operation. • Class E & F Power Amplifiers. • Class G & H Power Amplifiers. 5.7 Power Amplifiers Quiz. • Test your knowledge and understanding of Power Amplifiers. www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Amplifiers AMPLIFIERS MODULE 05.PDF 2 E. COATES 2007 - 2017 The voltage amplifiers described in Amplifiers Modules 1 to 4 can increase the amplitude of a signal
04/06/2017 · In this project I will show you why a class AB amplifier is pretty inefficient and how a class D amplifier on the other hand improves this efficiency. At the end I will show you how we can apply Class D Amplifier. Linear Mode Power Amplifiers – Class A, B, AB and class C are all linear mode amplifiers that have an output that is proportional to their input. Linear mode amplifiers do not saturate, fully turn-on or fully turn-off. Since the transistors are always conducting, heat is generated and continuously consuming power.
History. The first Class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. However, it had an output power of only 2.5 watts.The Sinclair X-20 in 1966 produced 20 watts, but suffered from the inconsistencies and limitations of the 2 Г— 210 W class-D power amplifier The TDA8953 single-chip Class D amplifier contains high-power switches, drivers, timing and handshaking between the power switches, along with some control logic. To ensure maximum system robustness, an advanced protection strategy has been implemented to
Class D: This operating class is a form of amplifier operation using pulse (digital) signals, which are on for a short interval and off for a longer interval. Power Amplifier Classes … • The power efficiency of an amplifier, defined as the ratio of power output to power input, improves (gets higher) going from class A to class D. Class D Power Amplifiers The D400 and D250 voice alarm power amplifiers comprise of two independent amplifier channels with 100 V output compatible with the Honeywell Voice Alarm System. The power amplifiers are controlled and monitored by the DOM4-8 (Digital Output Module) and DOM4-24 modules. Voice Alarm Key Features: l Power amplifier, 2